(page 1011(2))
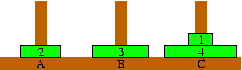
|
(page 1011(2)) |
|
| The Importance of Zero | |||||
|
So far we have discovered some interested things about the zero.
20 equals 1, in fact N0 is 1 for all N. 0 factorial equals 1, which some might find surprising. You might already know that you cannot divide anything by 0. The zero is a very important number, yet it took some time for it to be invented. The Zero Saga contains the following quotation from Professor Hossein Arsham: "The introduction of zero into the decimal system in the 13th century was the most significant achievement in the development of a number system, in which calculation with large numbers became feasible. Without the notion of zero, the descriptive and prescriptive modeling processes in commerce, astronomy, physics, chemistry, and industry would have been unthinkable. The lack of such a symbol is one of the serious drawbacks in the Roman numeral system. In addition, the Roman numeral system is difficult to use in any arithmetic operations, such as multiplication." In later pages, we see another important use of the zero.
The Invention of Zero |
Like many great inventions and discoveries, 0 is thought
to have been invented in multiple places at about the same time.
The Babylonians in about 300 B.C.E, the Mayas of Central America
in about 350 C.E. and the Hindus in about 450 C.E., all invented the
zero independently.
| If you are interested you could look at A Brief History of Zero or Invention of Zero. | |||
| hanoi11.qh - 1.2 - 05/10/02 |
|